Field of Application
- Non-contact measurement of flow velocities and turbulent flow variables
- High-Quality measurement of particle sizes and particle concentrations
- Due to strong focusing of the laser beams well suited for flow channels with low optical accessibility
Description
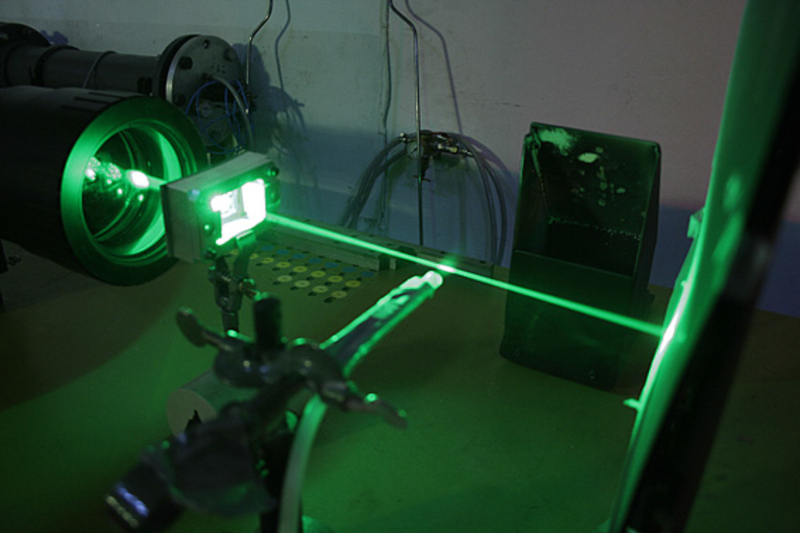
The Laser-2-Focus (L2F) or Laser-Transit method is based on the non-contact measurement of the time of flight of small particles between two parallel, strongly focused laser beams. In principle, this method can be compared to measuring the time of flight of particles between two light barriers. With the known distance of the focused laser beams and the measured time of flight, the flight velocity of the particles and thus indirectly the flow velocity is measured.
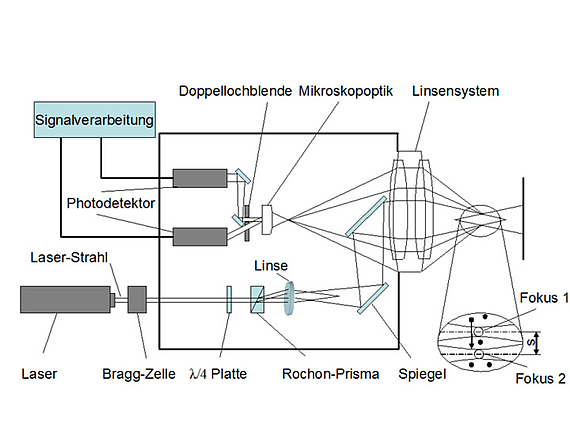
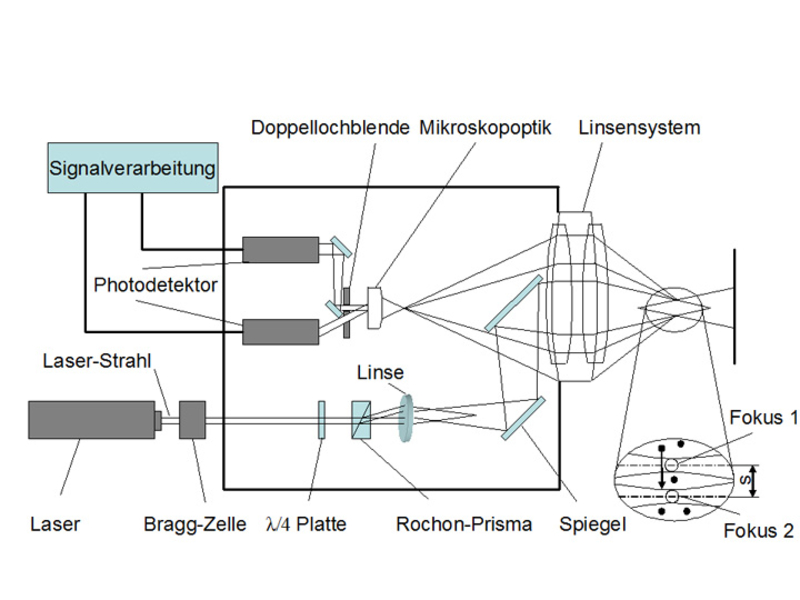
Two laser beams are strongly focused in a measurement volume. The particles passing through the measurement volume scatter the light as they pass through focus 1 and focus 2. These light pulses each correspond to a start and a stop pulse, whose time difference corresponds to the flight time of the particles. The light backscattered by the particles is detected by the outer part of the lens system and imaged in the image plane of a microscope optics. The light pulses are magnified by the microscope optics and fed to a double pinhole aperture. The subsequent optical setup passes the scattered light pulses of the start and stop pulses to the corresponding photodetector. These generate a voltage proportional to the scattered light intensity, which is fed to the signal processing and evaluation electronics.
By using the L2F at TFD, two components of the velocity vector are measured in the measurement plane spanned by the laser beams. The velocity measurement in one point in the flow is performed for a large number of particles. Thus, in turbulent flows, the mean flow velocities can be determined by applying statistical evaluation methods and the turbulent velocity components can be determined via the fluctuation widths.
Advantages of the L2F system compared to other optical measurement methods are:
- small optical access
- high signal-to-noise ratio
- very small measurement volume
- measurements in flow boundary layers possible
Independent extensions of the system at TFD:
- Qualitative measurement of particle concentration
- Qualitative measurement of particle size distributions
Measurement Parameter
- Flow velocity
- Particle concentration
- Particle size distribution